Deferred Expense
Deferred expense is a cost that has already been incurred, but which has not yet been consumed.
The cost is recorded as an asset until such time as the underlying goods or services are consumed; at that point, the cost is charged to expense.
A Deferred Expense is initially recorded as an asset, so that it appears on the balance sheet (usually as a Current Asset, since it is not used as of now and will probably be consumed within one year).
Introduced in Version 13
Before you start using deferred accounting you should be aware of the below settings which will give you more control over how you manage your deferred accounting

Automatically Process Deferred Accounting Entry: This setting is enabled by default. In case you don't want the deferred accounting entries to be posted automatically, you can disable this setting. If this setting is disabled, deferred accounting will have to be processed manually using Process Deferred Accounting
Book Deferred Entries Based On: Deferred expense amount can be booked based on two criteria. The default option here is "Days". If "Days" is selected, the deferred expense amount will be booked based on the number of days in each month and if "Months" is selected then it will be booked based on the number of months. For Eg: If "Days" is selected and $12000 expense has to be deferred over a period of 12 months, then $986.30 will be for the month having 30 days and $1019.17 will be booked for the month having 31 days. If "Months" is selected, $1000 deferred expense will be booked each month irrespective of the number of days in a month.
Book Deferred Entries Via Journal Entry: By default Ledger Entries are posted directly to book deferred expense against an invoice. In order to book this deferred amount posting via Journal Entry, this option can be enabled.
As an example of a Deferred Expense, Unico Plastics pays $10,000 in April for its May rent. It defers this cost at the point of payment (in April) in the prepaid rent asset account. In May, Unico Plastics has now consumed the prepaid asset, so it credits the prepaid rent asset account and debits the rent expense account.
Other examples of Deferred Expenses are:
Interest costs that are capitalized as part of a fixed asset for which the costs were incurred
Insurance paid in advance for coverage in future months
The cost of a fixed asset that is charged to expense over its useful life in the form of depreciation
The cost incurred to register the issuance of a debt instrument
The cost of an intangible asset that is charged to expense over its useful life as amortization
For an Internet Subscription, the amount is paid upfront and service is delivered every month. So it is Deferred Expense for the Customer.
Following is how you can configure Deferred Expense accounting in ActiveBooks to automate the process.
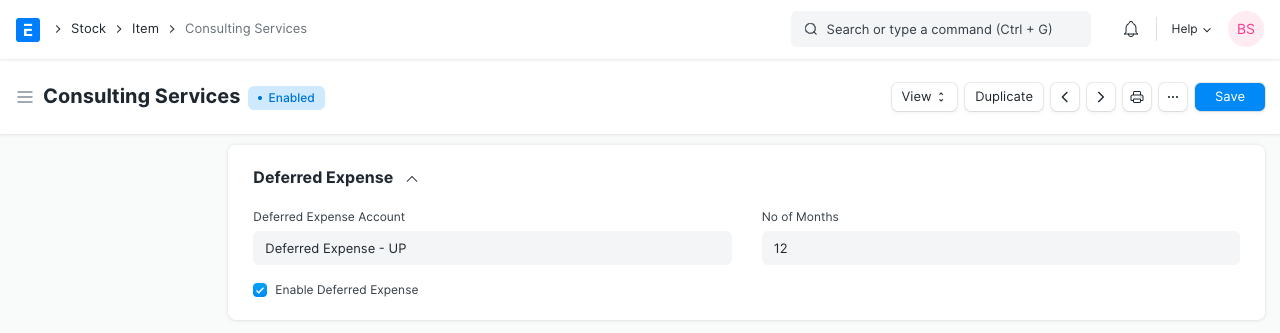
In the Item master, under Deferred Expense section, check field Enable Deferred Expense. In this section, you can also select a Deferred Expense account (Asset Account, preferably Current Asset) for this particular item and no. of months.
On creation of Purchase Invoice for the Deferred Expense Item, instead of posting in the Expense Account, Deferred Expense account (Asset account) is Credited by the purchase amount. Let's consider a simple example of an Internet subscription here:
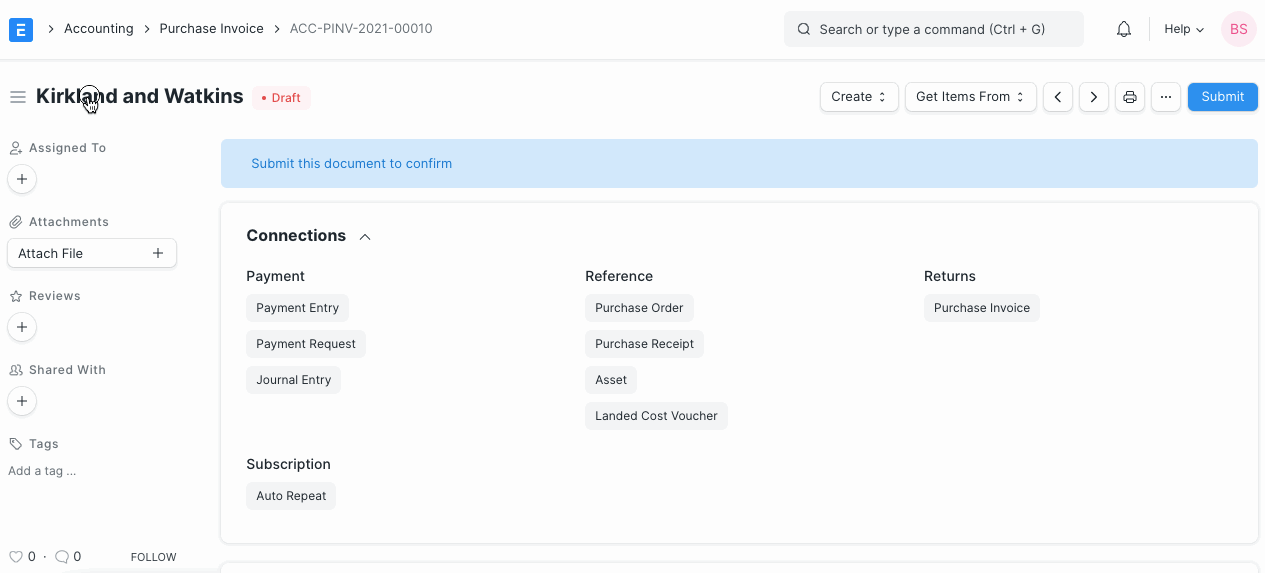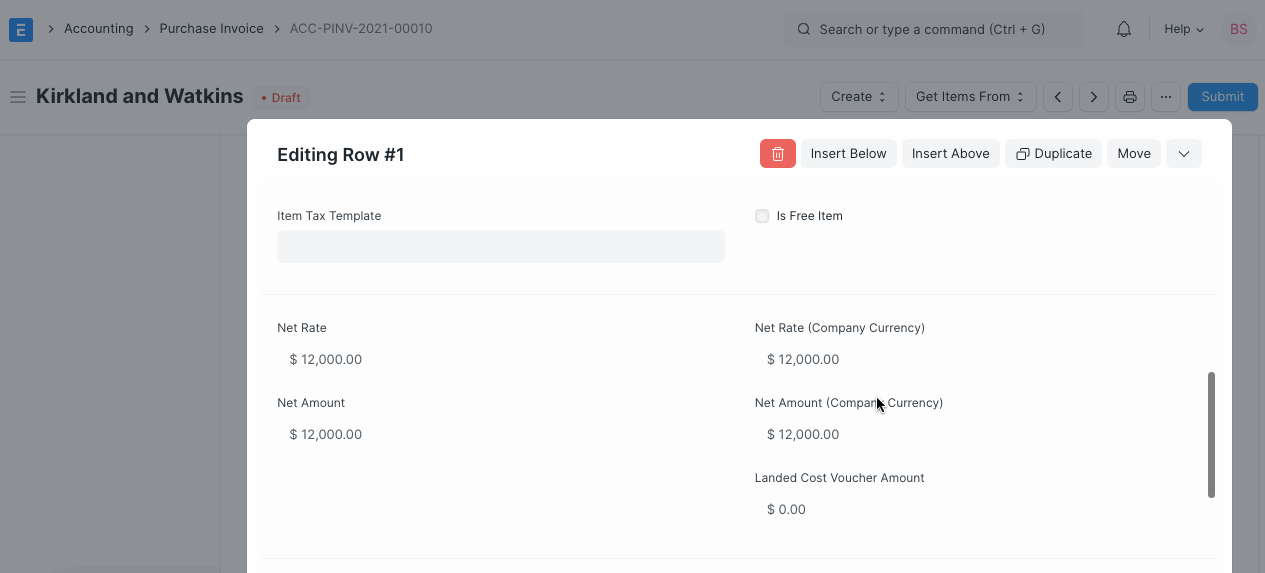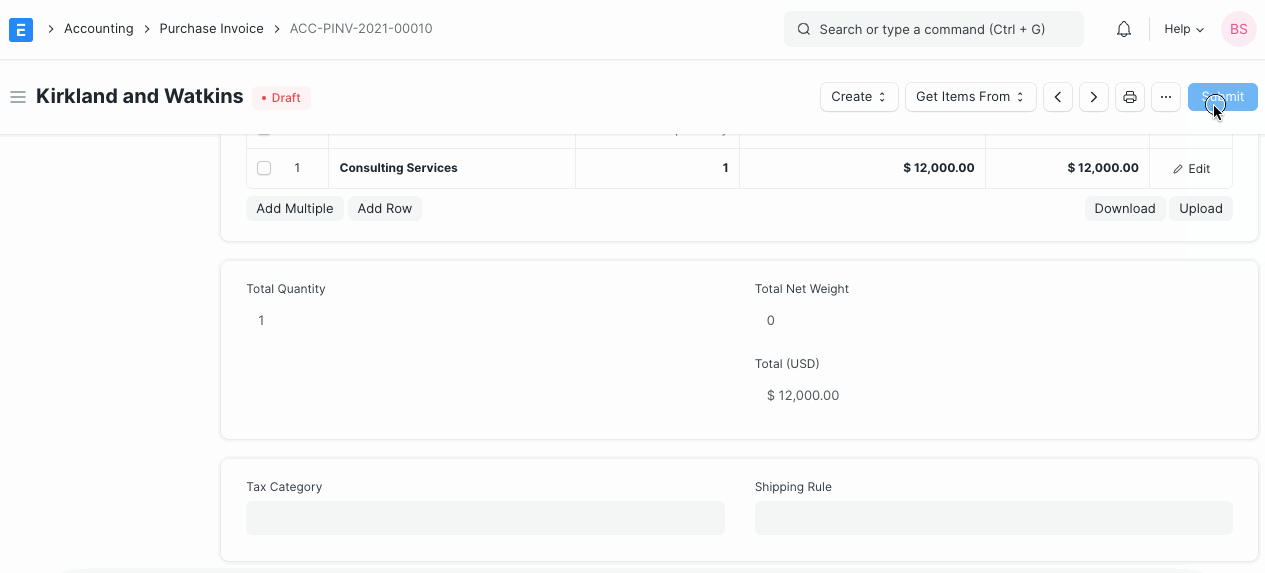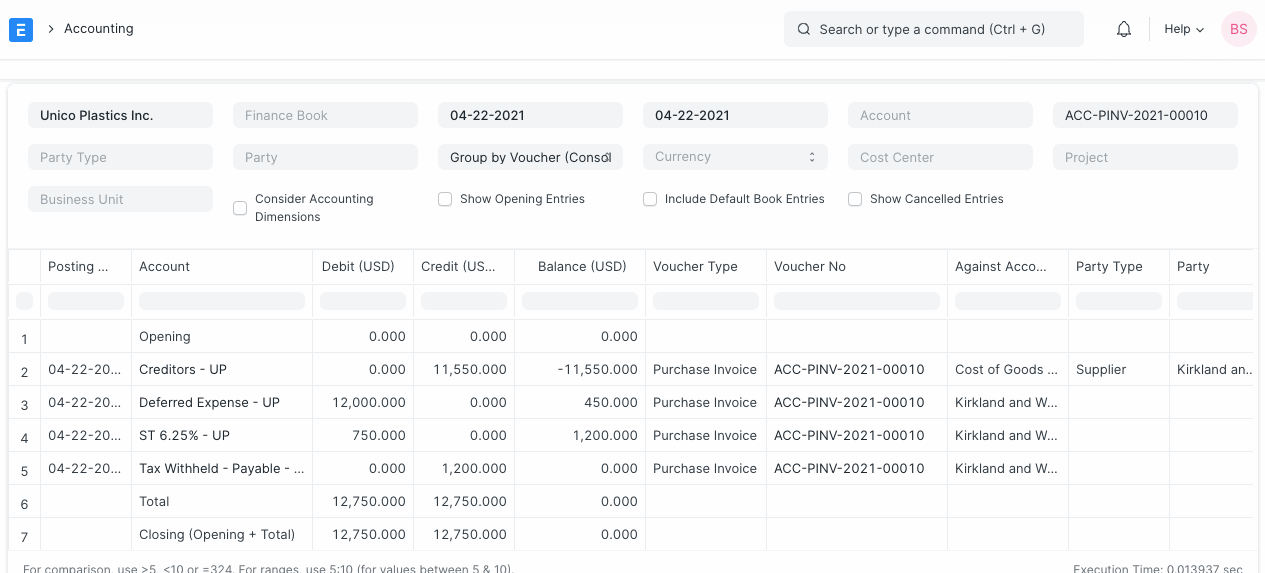
Based on the From Date and To Date set in the Purchase Invoice Item table, Journal Entries are created automatically at the end of each month. It debits the value from Deferred Expense account and credits Expense Account selected for an Item in the Purchase Invoice.
Last updated